Discover top causes of dispensing errors in community pharmacies & effective prevention strategies to ensure patient safety & medication accuracy.
Dispensing:
Dispensing is concerned with the preparation and supply of medicine
Community Pharmacies:
Community pharmacy, also known as retail pharmacy, is the most popular form of pharmacy that provides the general people with drugs and health advice. Today’s community pharmacists engage in a wide range of professional duties, including patient care that optimizes pharmaceutical treatment and promotes health, wellness, and disease prevention.
The dispensing procedure in community pharmacy is an important aspect of ensuring the quality use of medications, and it is one of the fundamental professional tasks of a pharmacist, along with patient counseling. Community pharmacists are increasingly involved in a wide range of patient care activities that optimize medication therapy and promote health, wellness, and disease prevention.
This practice emphasizes patient-oriented services rather than just drug product delivery. Community pharmacists serve as a primary source of scientifically accurate drug information and must advocate for the safe, appropriate, and cost-effective use of medications. The dispensing process in community pharmacy is a crucial aspect of effective medication use, alongside patient counseling, forming the core professional activities of a pharmacist.
The National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention (NCC MERP) defines medication error as “any preventable match that can also motive or lead to inappropriate medicine use or affected person damage whilst the medication is in the manage of the fitness care professional, patient, or consumer.
Medication errors are among the most common types of medical mistakes and can occur at multiple stages of healthcare. They include errors in prescribing, transcribing, dispensing, and administration. Such incidents may be linked to various aspects of professional practice, healthcare products, and systems, including order communication, product labeling, packaging, compounding, distribution, administration, education, monitoring, and patient use.
A discrepancy between the prescriber’s interpretable written order and the crammed prescription collectively with written adjustments made by means of capacity of the pharmacist pursuant to contact with the prescriber or in compliance with pharmacy coverage or the Errors that occur when distributing or promoting prescription to patient’s or patient’s agents.
definition of Dispensing Errors
There are so many definitions of dishing out mistakes such as: “Discrepancy between the prescriber’s written order and the stuffed prescription” or ” the Error that caught through a pharmacist observer after verification by way of the pharmacist”.
The kinds of shelling out blunders suggested in the literature are: wrong drug dispensed, incorrect power dispensed, incorrect form dispensed, incorrect extent dispensed, failure to grant drug, labeling error, incorrect drug identify on label, incorrect power on label, incorrect instructions & warnings on label, incorrect volume on label, incorrect affected person identify on label and absolutely wrong label.
Motives of Dispensing Errors:
The literature said the following motives of dispensing errors:
Comparable drug names, comparable packaging, staffing levels, bad handwriting, interruptions & distractions, design of dispensary, workforce inexperience, ambiguous directions, failure to check, lack of process, job dissatisfaction and bad communication.
Some more errors includes laptop software, noise; proximity of drugs on shelves, no breaks, failure to comply with fashionable operating procedures, empty stomach, tiredness, anxiety, lack of training, lack of concentration, lighting, lone worker, complicated prescription and lack of knowledge.
Therefore the purpose of this learn about was once to describe the dishing out mistakes that came about at some point of the dispensing system.
Management Of Dispensing Error Risk:
Two fundamental ideas summarize how the risk of dispensing blunders can be managed:
- Identifying traits of the pharmacy that help secure dispensing and making sure that these can operate.
- Identifying traits that undermine protected dispensing and making sure that these (or their effects) are controlled.
In the graph and everyday operation of dispensing, an necessary technique of managing chance is the implementation of hazard controls these are traits of the pharmacy that serve to give up an error from occurring, or from main to damage if it does occur. The greater various and dependable the controls, the higher organized the pharmacy will be to manipulate danger in dispensing.
In widespread terms, there are 4 kinds of controls in pharmacy:
- Administrative: Such as checklists, protocols, audits and appraisals,
- Social: Such as team, department or expert team conventions about work practice,
- Self: Such as private attitudes, preferences and habits,
- Technical: Such as laptop indicators and ‘lockouts’ (i.e. elements of the gear that enable them to be used solely in a precise and right manner.
Generally, the most tremendous controls are these that get rid of blunders at supply (e.g. via disposing of a company of medicine that is especially inclined to being distributed in error).
The subsequent most high quality controls are these that comprise the traits that may want to provide upward thrust to an error (e.g. by means of proscribing monitored dosage gadget meting out to specific dispensary locations).
The weakest controls are commonly these that area the onus on humans to take manipulate movements themselves (e.g. setting a label subsequent to an object that is inclined to being burdened for another).
This does no longer suggest that solely these controls that remove blunders at supply are worthwhile, however it does imply that relying solely on a small quantity of weaker controls will restrict the capacity to deal with the vary of mistakes that should occur. It is vital to be aware that some of the methods in which blunders would possibly show up may also now not be at once obvious.
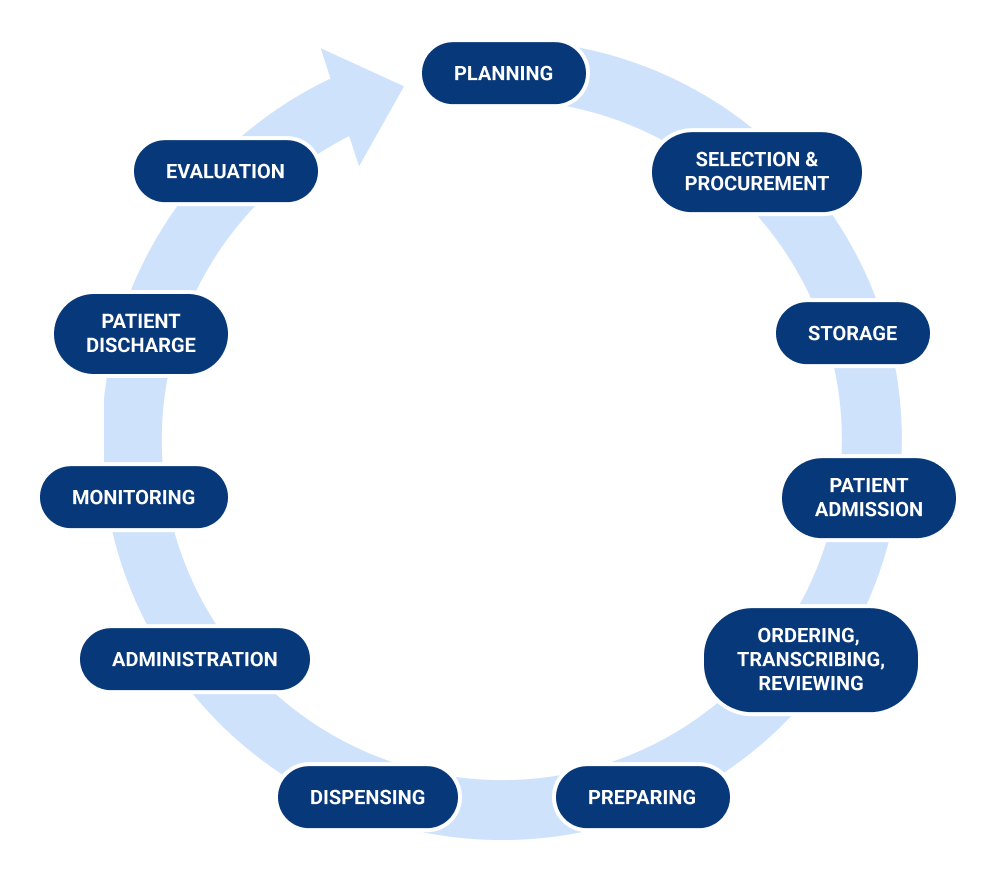
Dispensing Error:
Dispensing errors are defined as any inconsistencies or deviations from the prescription order, such as dispensing the incorrect drug, dose, or dosage form, dispensing the incorrect quantity, inappropriate, incorrect, or inadequate labeling.
Also confusing, or inadequate medication use instructions, and incorrect preparation, packaging, or storage of medication before dispensing are all considered as dispensing errors.
Dispensing Errors In Community Pharmacies:
The following are the most often reported mistakes in community pharmacies:
- Inaccurate dose or strength
- Incorrect medicine
- Incorrect formulation
- Inaccurate quantity of a medicine
- Wrong label
CAUSES OF DISPENSING ERRORS:
The causes of dispensing errors are discussed below:
1) Use Of Expired Products:
Usually arises as a result of incorrect preparation storage, leading in degradation or the usage of expired items.
2) Wrong Preparation:
This mistake is most commonly seen during compounding or other types of preparation prior to final administration. Choosing the inappropriate diluent to reconstitute is one of the examples.
3) Wrong Strength:
Incorrect strength might occur at any step throughout the drug procedure. It frequently happens as a result of human mistake when comparable bottles or syringes with the wrong strength are used.
4) Wrong Dosage Form:
This happens when a community pharmacist makes formulation of incorrect dosage form and patient is given a different dose form than what was recommended, such as immediate-release instead of extended-release.
5) Incorrect Labeling:
Wrong label means incorrect intake of dose. This mistake involves overdosing, under dosing, and administering an excess dosage.
An improper dosage happens when an unsuitable or different medicine dose than what was authorized is administered, errors of omission occur when a planned dose of medication is not administered, and a drug is administered via an incorrect route. These types of errors are usually caused by imprecise and wrong labeling.
6) Distractions:
Distractions are also most likely to cause errors when a community pharmacist is preparing a formulation.
7) Improper Patient Counseling:
Improper communication or counseling with a patient is also a major cause of dispensing error in community pharmacies as the patient can take wrong dose, and can take the medicine via inappropriate route.
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE:
Medication mistakes are a frequent problem in healthcare, costing billions of dollars and causing considerable morbidity and mortality. Despite national attention, drug delivery mistakes continue to be a pervasive concern.
The most effective way to improve patient safety is to create a multifaceted education and preventive approach. The importance of healthcare practitioners working as a team and communicating, as well as encouraging patients to be better aware about their prescriptions, should be emphasized. Medication dispensing mistakes can be decreased with a safety culture.
WHAT CAUSES DISPENSING ERRORS?
Currently the only blame for such errors lies on to mankind and their input, from assessing the prescriptions to interpreting them, looking for the items or providing the best possible alternatives to fulfilling the patient’s order correctly. According to a research it was found that the accuracy of a particular order mostly lays onto the individual’s ability to comprehend data and deliver the best based on the demand. Other than that the setting of a place also plays an important role which is broken into 5 categories mentioned below:
- The people involved which include, pharmacists, technicians, patients, prescriber, dispensers.
- Tasks carried out properly which include arranging the stock to ones reach, reading of scripts.
- The lighting, sound or emission of heat at a particular environment.
- The usage of technology and tools e.g. Barcode scanners, measuring devices, patient medication records.
- The center or organization within which dispensing occurs including communication networks, allocation of responsibilities, organizational priorities.
It was also noted that the setting of a place usually plays a major role in safe and sound dispensing with the elimination of any errors helping to fasten the tasks. Although certain problems can arise in relation to the above given points. In the research held these points are quite equal to the ‘blunt end’ and ‘error producing conditions’.
As per the research if large amounts of these vulnerabilities come together then the risk for an error increases. But there are reasons where these vulnerabilities shall be overlooked like:
- The first being that the records for the patient’s medication might not be up to date which include changes in medicines being used or that prescribed.
- The staff has become quite used to working in a cluttered environment.
- It is not important that vulnerability may always cause error as staff may be used to working under such conditions with no negative impact.
- The vulnerability may be overlooked following previous incidents that did not go into check.
It is although necessary to reflect upon such situations to avoid the occurrence of a mishap.
Methods:
To Carry Out Study, Design And Setting:
A prospective study is carried out in a certain region, within a city. A sampling frame of all the community pharmacies is made and the eligibility is checked.
Data Collection Procedure:
Data is collected over a span of a few months. Dispensing error in this context is defined as “Errors that occur when distributing or selling prescription to patient’s or patient’s agents”.
Dispensing errors that were detected during or after the dispensing process were recorded by the pharmacy dispensers using a data collection form. Detecting and reporting of dispensing errors, types and causes of dispensing errors were explained to the participated pharmacy dispensers before starting the study through workshops, educational materials and training.
Statistical Analysis:
The date is interpreted through special software.
Ethical Approval:
The survey is approved through a qualified research place.
Result:
The five community pharmacies employed two community pharmacists and eight pharmacy technicians. They were Yemen males who had completed their education. The average age of the respondents was 24.70± 4 years.
The two of them Pharmacists had more than five years of experience, and Technicians in the pharmacy had less than five years of experience and about 5680 prescriptions were dispensed and checked at the five community pharmacies, according to the findings. In this study, 47 dispensing errors (0.82 percent) were reported. Table 1 shows the many types of dispensing errors.
Types Of Dispensing Errors (N=47)
| TYPES OF ERRORS | N (%) |
| Wrong dosage form | 33 (70.2) |
| Wrong strength | 5 (10.6) |
| Wrong quantity | 4 |
| Drug available in the pharmacy but not given | 3 |
| Wrong drug | 2 |
Prescriptions with bad handwriting, identical pharmaceutical packaging, and medication on shelves not ordered appropriately, similar drug names, and a severe work load were the most commonly factors mentioned in this study as contributing to dispensing problems.
Discussion:
The majority of pharmacy dispensers in this survey (eight out of ten) were pharmacy technicians, which is consistent with a prior report showing the ratio of pharmacists working in pharmacies is increasing. Yemen has a large number of community pharmacies compared to the total number of pharmacies in the country. The number of technicians is modest.
The findings of this investigation revealed that every pharmacist. Male pharmacists worked in the five community pharmacies. This is comparable to earlier research, and it could be because of it. The percentage of male pharmacy students is approximately 70%. Yemen’s total student population and cultural difficulties
In this investigation, a total of 47 dispensing errors were reported. Inappropriate dose form (33/47), followed by wrong strength (5/47), and wrong quantity (4/47) were the most prevalent dispensing errors. (3/47), as well as a medicine that was accessible in the pharmacy but was not given. Finally, the study found that the least common dispensing error is was the incorrect medicine (2/47).
In this study, we looked at the frequency, types, and causes of dispensing errors. Study differs from what has been documented in other studies around the world. It’s possible that the disparity is attributable to the study’s context and methods.
According to the conclusions of this study, the following factors contributed to dispensing errors: Prescriptions with sloppy handwriting, packaging that looks identical to other medications, and medication that isn’t on the shelves correctly organized, similar medicine names, and job load.
Poor handwriting is cited as a primary source of error in this study. Handwritten prescription errors might cause pharmacy dispensers to misread the prescription, resulting in drug misuse. Prescriptions of high quality are critical in order to reduce drug distribution errors, Prescription recommendations should be followed by doctors. Writing for the improvement of patient care.
Prescriptions in general should include factual and relevant information about the patient and the drug given. Prescriber’s name, address, phone number, and signature; patient’s name, address, age, and weight; prescription date; drug name, formulation, strength, dose, frequency of administration, quantity prescribed, why given, and instructions for usage should all be included on all prescriptions.
The key to minimizing and preventing dispensing errors is to teach and train health care providers about dispensing errors, as well as collaboration and communication.
Conclusion:
The most prevalent sort of dispensing error recorded in this study was wrong dosage form, followed by wrong strength, wrong quantity, and medicine present in the pharmacy but not supplied, and inappropriate drug. It is strongly recommended that the incidence of dispensing errors, as well as the types and causes of dispensing errors, be studied in additional Yemen cities.
Investigate the effects of various treatments to improve dispensing quality, with a focus on decreasing and preventing dispensing errors. The key to minimizing and preventing dispensing errors is to teach and train health care providers about drug errors, as well as collaboration and communication.
References:
https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/24883
Dispensing Errors in Community Pharmacies: A Prospective Study in Sana’a, Yemen Archives of Pharmacy Practice ¦ Volume 9 ¦ Issue 4 ¦ October – December 20181